Stop Loss Strategies: Protect Your Forex Trades Like a Professional Trader

A stop loss is your trading insurance policy. It's the point where you admit you're wrong and exit the trade before losses become catastrophic. While most retail traders move their stops against them or avoid using them entirely, professional traders know that proper stop loss placement is the difference between surviving as a trader and losing everything.
Understanding Stop Loss Fundamentals
What is a Stop Loss?
A stop loss is a predetermined price level at which you automatically exit a losing trade. It's set when you enter the trade and should never be moved further against your position.
✅ Professional Stop Loss Use
- Set before entering the trade
- Never moved against position
- Based on technical analysis
- Accepts that losses are part of trading
- Protects account capital
❌ Amateur Stop Loss Mistakes
- No stop loss at all
- Moving stops against position
- Setting stops too close (whipsaw)
- Emotional stop placement
- Hoping price will "come back"
Why Stop Losses Are Non-Negotiable
- Capital Preservation: Prevents single trades from destroying your account
- Emotional Control: Removes decision-making from losing trades
- Risk Management: Ensures consistent risk per trade
- Professional Trading: Required by successful trading strategies
- Sleep Peace: Allows you to trade without constant monitoring
Types of Stop Loss Orders
1. Market Stop Loss
📊 Market Stop Loss (Stop Market Order)
How it works: Order executes at market price when trigger price is hit.
Pros: Always executes if price reaches stop level
Cons: Execution price may slip during volatile periods
Best for: Most trading situations where slippage is acceptable
2. Limit Stop Loss
📋 Limit Stop Loss (Stop Limit Order)
How it works: Places a limit order when trigger price is hit.
Pros: No slippage if limit order fills
Cons: May not execute during volatile markets
Best for: Illiquid pairs or extreme volatility situations
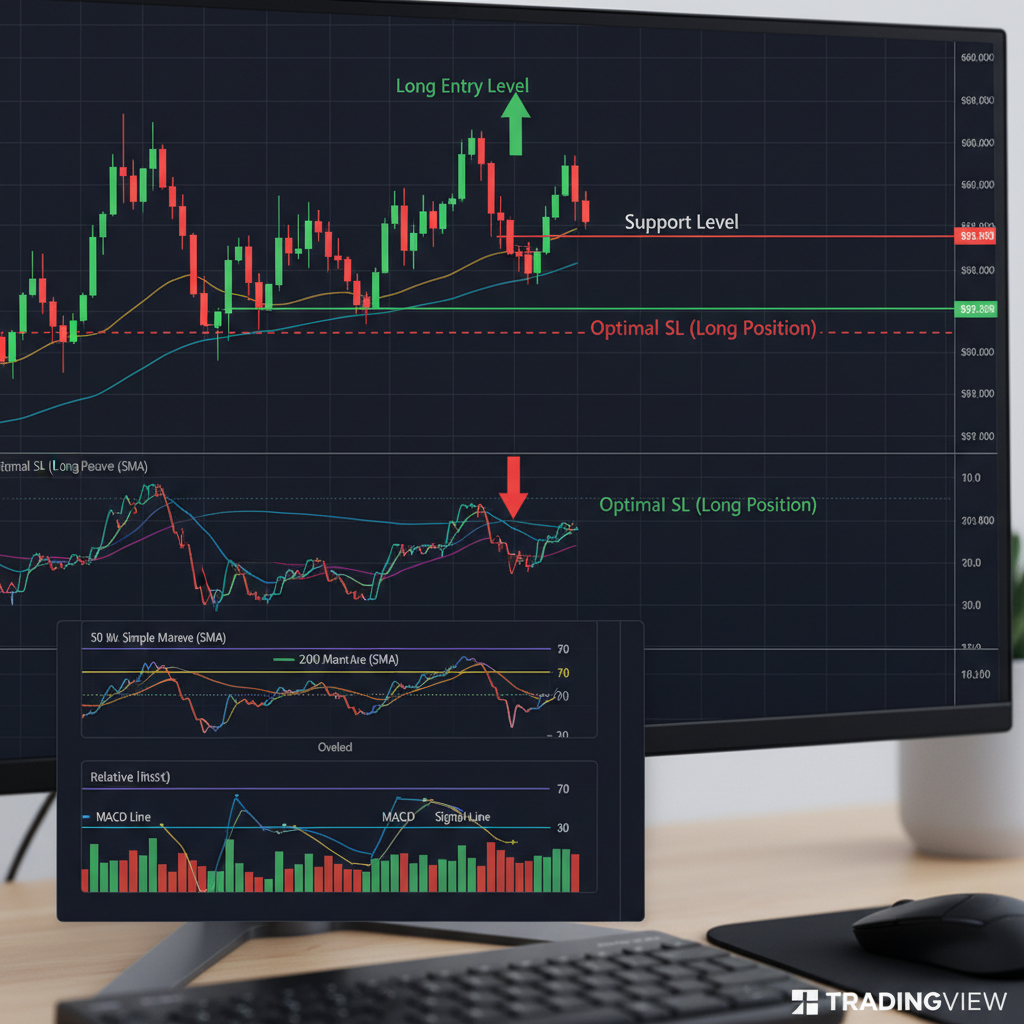
Stop Loss Placement Strategies
1. Technical Stop Loss Placement
🎯 Technical Analysis-Based Stops
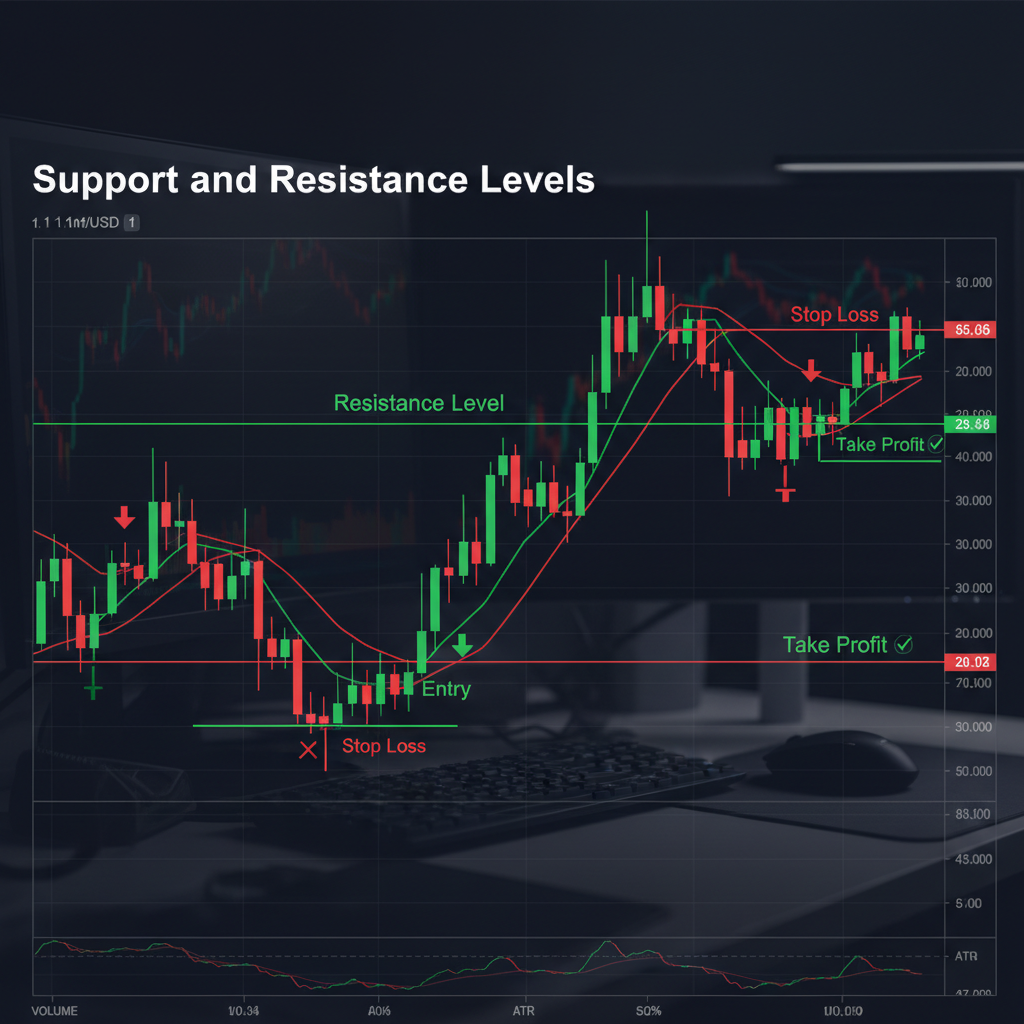
Support and Resistance Stops
- Long Positions: Place stop below recent support level
- Short Positions: Place stop above recent resistance level
- Buffer: Add 5-10 pips beyond the level to avoid being stopped by normal price noise
Chart Pattern Stops
- Head and Shoulders: Stop above/below the pattern's highest/lowest point
- Triangles: Stop beyond the opposite side of the triangle
- Flags/Pennants: Stop beyond the pole or flag pattern
Moving Average Stops
- Long Positions: Stop below 20 or 50-period moving average
- Short Positions: Stop above 20 or 50-period moving average
- Multiple MA Stop: Stop below/above several moving averages
2. Percentage-Based Stop Loss
📈 Fixed Percentage Stops
Concept: Set stop loss at a fixed percentage from entry price.
| Stop Percentage | Major Pairs (1.1000) | JPY Pairs (110.00) | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1% | 11 pips | 110 pips | Tight scalping stops |
| 2% | 22 pips | 220 pips | Day trading stops |
| 3% | 33 pips | 330 pips | Swing trading stops |
| 5% | 55 pips | 550 pips | Position trading stops |
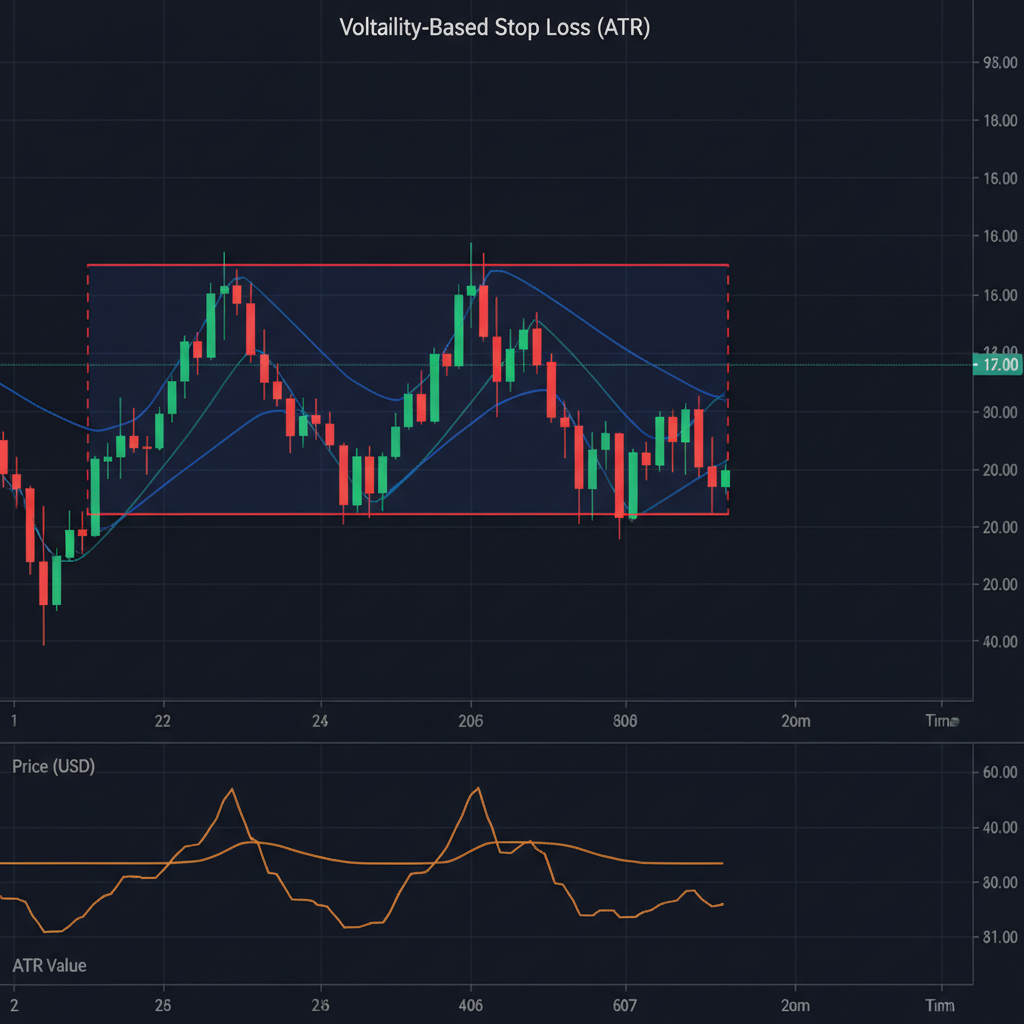
3. Volatility-Based Stop Loss
📊 Average True Range (ATR) Stops
Concept: Set stop loss based on current market volatility.
ATR Stop Calculation
- Calculate 14-period ATR for the currency pair
- Multiply ATR by desired multiplier (1.5, 2, or 3)
- Add/subtract from entry price for stop placement
ATR Multiplier Guidelines
- 1.5 × ATR: Tight stops for low volatility
- 2 × ATR: Standard stops for normal volatility
- 3 × ATR: Wide stops for high volatility
Long position at 1.1000: Stop = 1.1000 - (25 × 2) = 1.0950
Stop distance: 50 pips
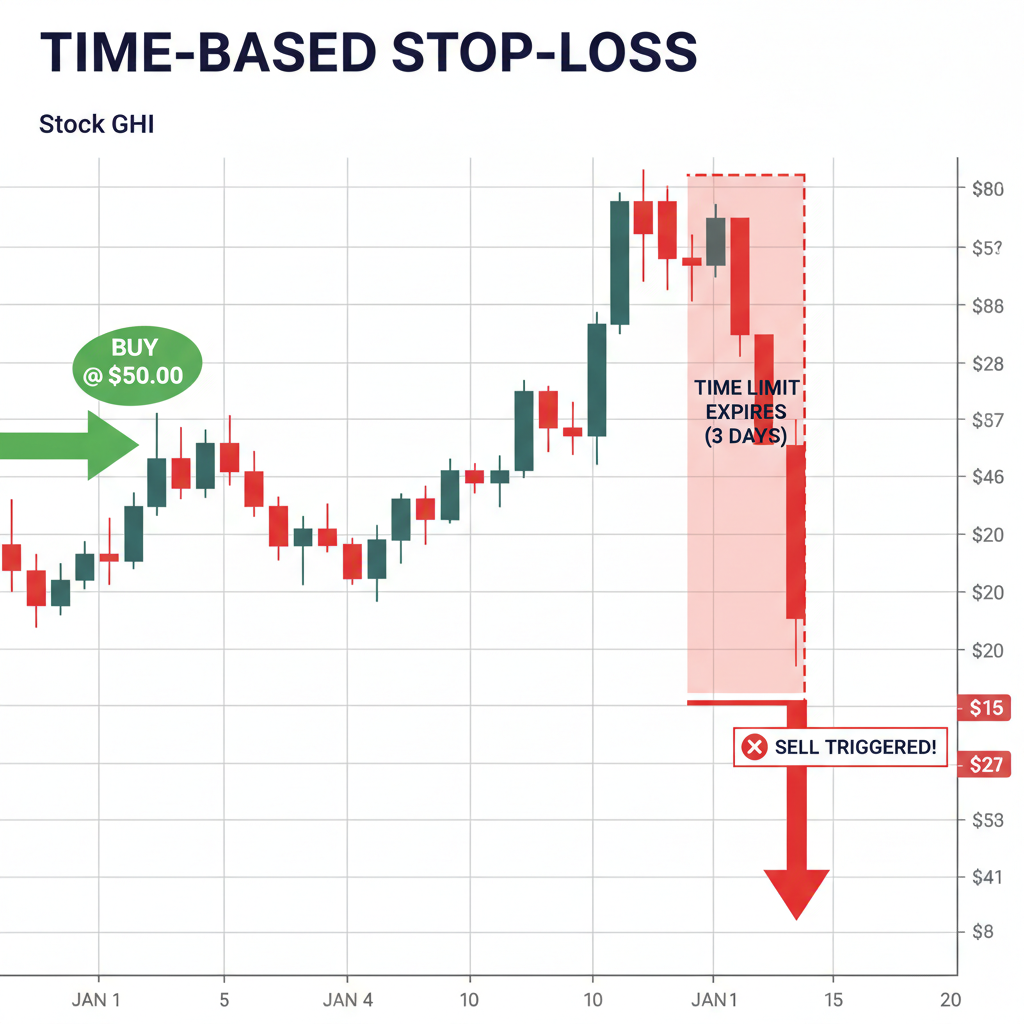
4. Time-Based Stop Loss
⏰ Time Stop Strategy
Concept: Exit trade if no profit is achieved within a specified time frame.
- Scalping: Exit after 30-60 minutes if no movement
- Day Trading: Exit before market close if no progress
- Swing Trading: Exit after 3-5 days if stuck
Best for: Avoiding trades that "go nowhere" and tying up capital.
Advanced Stop Loss Techniques
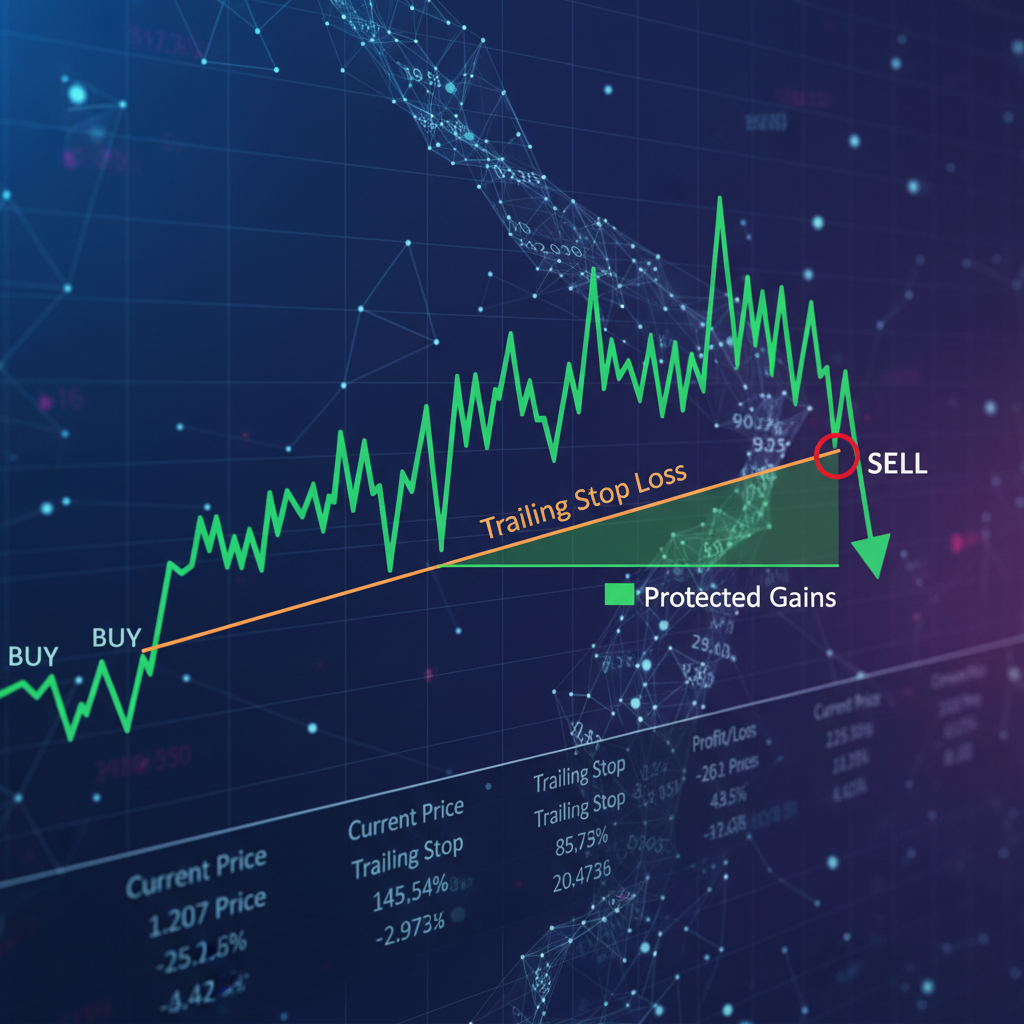
1. Trailing Stop Loss
🔄 Trailing Stop Implementation
Concept: Move stop loss to lock in profits as trade moves favorably.
Trailing Stop Methods
- Fixed Pips Trailing: Move stop up/down by fixed amount (e.g., 20 pips)
- Percentage Trailing: Trail by percentage of current price
- ATR Trailing: Trail by ATR multiplier (e.g., 2× ATR)
- Technical Trailing: Trail behind moving averages or trend lines
Trailing Stop Examples
Long EUR/USD at 1.1000
Trail 20 pips: Price moves to 1.1020 → Stop moves to 1.1000
Price moves to 1.1040 → Stop moves to 1.1020
Long EUR/USD at 1.1000, ATR = 25 pips
Trail 2× ATR = 50 pips
Price at 1.1050 → Stop = 1.1000
Price at 1.1100 → Stop = 1.1050
2. Hidden Stop Loss
👻 Psychological Stop Placement
Concept: Place stops at levels where they won't be easily spotted by other traders.
- Below obvious support: Others might place stops there
- At round numbers: 1.1000, 1.2000 attract stops
- At Fibonacci levels: Many traders use Fibonacci stops
- Above/below obvious levels: Not at the level, but just beyond
Benefits: May avoid being "stopped out" by other traders' activity.
3. Partial Stop Loss
✂️ Partial Position Exits
Concept: Close portions of position at different profit levels.
Partial Exit Strategy
- Enter position with full size
- Take partial profit at first target (close 25-50%)
- Move stop to breakeven on remaining position
- Let remaining position run with trailing stop
Target 1: 1.1050 → Close 0.5 lots, move stop to 1.1000
Target 2: 1.1100 → Close remaining 0.5 lots
Result: Locked in 25 pips profit on half position, risk-free on remainder
Stop Loss Placement by Trading Style
Scalping Stop Loss
⚡ Scalping Stop Strategy
- Stop Distance: 5-15 pips typical
- Placement: Just beyond support/resistance levels
- Reasoning: Tight stops work due to quick entries/exits
- Risk: High risk of being whipsawed out
Day Trading Stop Loss
📈 Day Trading Stop Strategy
- Stop Distance: 20-50 pips typical
- Placement: Beyond key intraday levels
- Reasoning: Balance between room for noise and risk control
- Adjustment: May use wider stops during high volatility periods
Swing Trading Stop Loss
📊 Swing Trading Stop Strategy
- Stop Distance: 50-150 pips typical
- Placement: Beyond swing highs/lows or major S/R levels
- Reasoning: Allow for normal market noise and fluctuations
- Monitoring: Less frequent monitoring required
Position Trading Stop Loss
🏗️ Position Trading Stop Strategy
- Stop Distance: 200-500+ pips typical
- Placement: Beyond major long-term support/resistance
- Reasoning: Allow for major market swings and fluctuations
- Management: Use trailing stops as position progresses
Stop Loss Best Practices
Professional Guidelines
✅ Golden Rules of Stop Loss Trading
- Set stops before entering: Never enter without knowing your exit
- Never move stops against you: If you're wrong, accept the loss
- Accept small losses: Big losses come from not cutting losses short
- Respect your stops: Don't cancel them or move them further away
- Consider market conditions: Volatile markets need wider stops
- Use appropriate position size: Stop distance affects position size

Stop Loss Mistakes to Avoid
- Setting stops too close: Gets stopped out by normal market noise
- Setting stops too wide: Increases risk per trade unnecessarily
- Moving stops against position: Turns small losses into big losses
- Emotional stop placement: Setting stops based on hope, not analysis
- Not accounting for spreads: Consider bid-ask spread in stop placement
- Ignoring volatility changes: Static stops in dynamic markets
- Setting stops at obvious levels: May get triggered by stop hunting
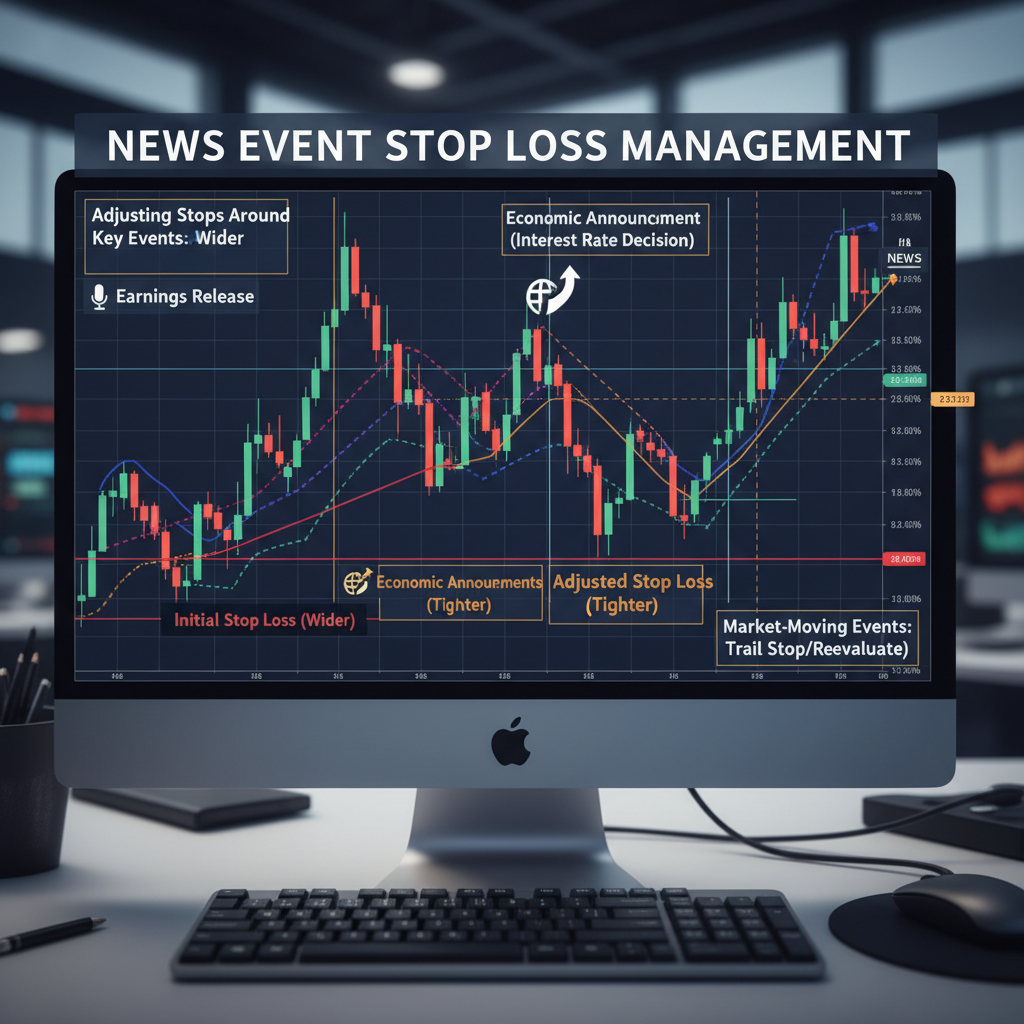
Stop Loss During News Events
High-Impact News Stop Strategy
📰 News Event Stop Loss Management
Before High-Impact News
- Option 1: Close positions 30 minutes before news
- Option 2: Widen stops to accommodate volatility
- Option 3: Reduce position size to lower risk
- Avoid: Entering new positions before major news
During High-Impact News
- Wider stops (2-3× normal size)
- Be prepared for gap moves
- Don't panic if stop gets triggered
- Wait for volatility to settle before re-entering
After High-Impact News
- Assess new market structure
- Set new stops based on updated levels
- Look for re-entries at better prices
Stop Loss Technology and Tools
Broker Stop Loss Features
Automated Stops
- Guaranteed stops: No slippage, higher cost
- OCO orders: One-cancels-other functionality
- Trailing stops: Automatic trailing capability
- Breakeven stops: Move to entry when in profit
Advanced Order Types
- If-then orders: Conditional stop placement
- Bracket orders: Entry + stop + target
- OCO brackets: Stop and target cancel each other
- Iceberg orders: Partial position exits
Platform Stop Loss Tools
- MetaTrader 4/5: Stop loss, take profit, trailing stops
- cTrader: Advanced order management
- NinjaTrader: Professional stop loss options
- TradingView: Strategy-based stop placement
Creating Your Stop Loss Strategy
🎯 Step-by-Step Stop Loss Plan
Step 1: Define Your Trading Style
- Scalper: 5-15 pip stops, tight management
- Day Trader: 20-50 pip stops, intraday focus
- Swing Trader: 50-150 pip stops, multi-day holds
- Position Trader: 200-500+ pip stops, long-term trends
Step 2: Choose Your Stop Method
- Technical Stops: Based on chart levels (recommended)
- ATR Stops: Based on volatility (good for beginners)
- Percentage Stops: Fixed percentage from entry (simple)
- Time Stops: Exit after time period (complementary)
Step 3: Set Stop Loss Rules
- Always set stop before entering trade
- Never move stop against position
- Consider market volatility in stop distance
- Use trailing stops for profitable trades
- Review and adjust stop placement monthly
Stop Loss Psychology
Overcoming Stop Loss Resistance

😰 Fear-Based Stop Loss Issues
- Fear of being wrong about the trade
- Fear of missing out on profits
- Hope that price will reverse
- Reluctance to accept loss
🧠 Professional Mindset
- Accepting that losses are part of trading
- Understanding that being wrong is okay
- Focusing on overall performance, not single trades
- Knowing that small losses preserve capital

Conclusion
Stop loss placement is the foundation of professional forex trading. It's what separates amateur traders who hope their trades will work out from professional traders who know exactly when they're wrong and accept that loss quickly.
Mastering stop loss strategies requires:
- Understanding different stop loss types and their applications
- Choosing appropriate stop methods for your trading style
- Setting stops based on technical analysis, not emotion
- Never moving stops against positions, regardless of hope
- Using trailing stops to lock in profits on winning trades
Remember that stop losses are not where you lose money—they're where you preserve your trading career. Every professional trader has lost money on individual trades, but they've survived because they cut losses short and let profits run.

No comments